4 Which of the Following Lenses Is a Converging Lens
The same reasoning applies to the diverging lenses as shown in part b. Compound microscope objects uses two converging lenses to produce two images the second of which is virtual magnified and inverted.

Quiz What Do You Know About Thin Converging Lens Trivia Questions Proprofs Quiz
The ray that passes through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract and travel parallel to the principal axis.

. To find the location and size of the image formed we. Once these incident rays strike the lens refract them according to the three rules of refraction for converging lenses. Use a straight edge to accurately draw its path.
A ray that enters a diverging lens by heading toward the focal point on the opposite side exits parallel to the axis. For a diverging lens the point. The lens is a transparent material which is bound by two surfaces.
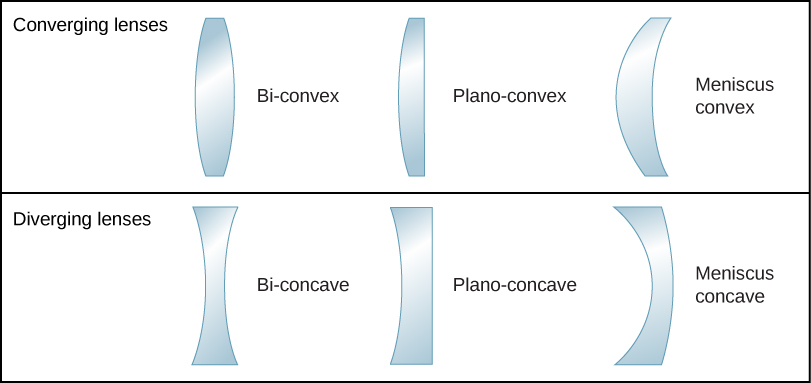
A ray entering a converging lens through its focal point exits parallel to its axis. A convex lens is also called a converging lens while a concave lens is known as a diverging lens due to its ability to converge and diverge. Concave lens is the lens that is thicker around the edges while the convex lens is the one with thick centres.
The ray that traveled parallel to the principal. The arity of the new function is the same as the arity of the longest branching function. Unlike conventional cylindrical lenses a single flat lens can be metamorphosed to converging and diverging lenses which only depends on the helicity of the CP light.
When invoked this new function is applied to some arguments and each branching function is applied to those same arguments. For a converging lens the point at which the rays cross is the focal point F of the lens. If an object 18 millimeters high is placed 12 millimeters from a diverging lens and the image is formed 4 millimeters in front of the lens what is the height of the image.
Accepts a converging function and a list of branching functions and returns a new function. The overall effect is that light rays are bent toward the optical axis for a converging lens and away from the optical axis for diverging lenses. Below is an.
It has a principal axis principal focus centre of curvature of lens aperture and optical centre. The images obtained from these lenses can be either a real image or a virtual image. The results of each branching function.
Lenses are the optical tools that have the ability to converge or diverge a beam of light through the process of refraction. There are two types of lenses they are a convex lens and a concave lens. Consider an object some distance away from a converging lens as shown in Figure 1627.
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Converging And Diverging Lens If One S Eyeball Is Too Long Or Too Wide The Light Rays Will Not Meet A Science Lessons Elementary Learn Physics Basic Physics

Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 4 Converging Lens Physics Classical Physics Physics Notes
Comments
Post a Comment